Email spoofing, when malicious actors disguise their email address to appear as someone else, is a common tactic used in phishing attacks, business email compromise (BEC), and other scams. To combat this threat, email authentication protocols like Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) were developed. However, these protocols alone don’t provide complete protection. This is where DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, comes into play.
What is DMARC?
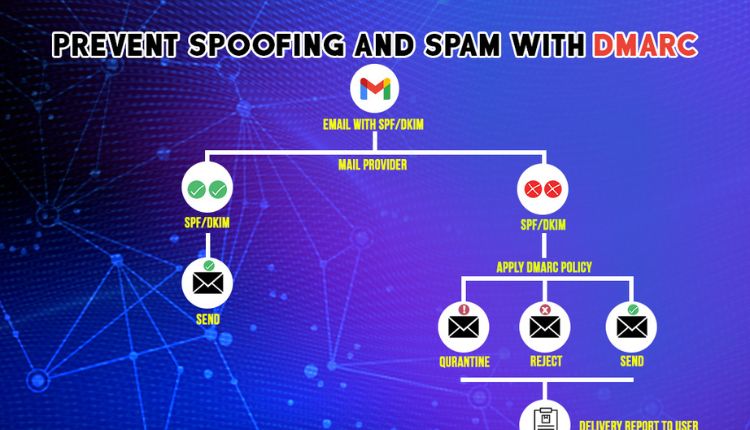
DMARC builds upon SPF and DKIM by providing a reporting mechanism for email authentication. It allows domain owners to instruct receiving mail servers (like Gmail) on how to handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. This empowers domain owners to take control of their email reputation and protect their users from spoofing attacks.
Why is DMARC important for Gmail users?
Since February 1, 2024, Google requires all email senders who want their messages to reach Gmail inboxes to meet specific email authentication requirements, including implementing DMARC for Gmail. This is a significant step towards enhanced email security for Gmail users, as it significantly reduces the risk of receiving spoofed emails that appear to be from legitimate individuals or organizations.
How does DMARC work with Gmail?
Here’s a breakdown of the interaction between DMARC and Gmail:
- DMARC record setup: A domain owner publishes a DMARC record in the Domain Name System (DNS). This record specifies:
- Policy: This instructs receiving mail servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. Common policy options include:
- p=none: Monitor but take no action.
- p=quarantine: Quarantine unauthenticated emails.
- p=reject: Reject unauthenticated emails.
- Reporting: This specifies whether receiving mail servers should send reports about email authentication results to the domain owner.
- Policy: This instructs receiving mail servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. Common policy options include:
- Email sending: When an email is sent from a domain, Gmail performs SPF and DKIM checks to verify the sender’s legitimacy.
- DMARC evaluation: If the email fails SPF or DKIM checks, Gmail checks the domain’s DMARC record to determine the specified policy.
- Action based on policy: Based on the policy:
- p=none: Gmail delivers the email normally, but sends reports to the domain owner.
- p=quarantine: Gmail quarantines the email, preventing it from reaching the user’s inbox but allowing the domain owner to review it.
- p=reject: Gmail rejects the email entirely, preventing it from reaching the user’s inbox.
Benefits of DMARC for Gmail users
- Reduced phishing and spam: DMARC significantly reduces the risk of receiving spoofed emails that appear to be from legitimate senders, making it harder for attackers to launch phishing and BEC attacks.
- Improved email security: By enforcing email authentication, DMARC helps ensure that only authorized senders can send emails using a particular domain, enhancing overall email security for Gmail users.
- Increased trust in email communication: Knowing that emails are coming from legitimate sources fosters trust in email communication, allowing users to feel more confident when interacting with emails.
How to check if your domain has DMARC enabled
You can use online tools like a DMARC checker to check if a domain has a DMARC record published and what policy it enforces.
If you’re a domain owner, implementing DMARC is a straightforward yet impactful step towards protecting your email reputation and safeguarding your users. Several free and paid tools, like PowerDMARC, can help you check your DMARC record status and guide you through the implementation process. Don’t wait – take control of your email security and enable DMARC today!